Agile Roles in SAFe Explained
Introduction to Agile Roles in SAFe
In the ever-evolving technological landscape, Agile development methodologies, such as Scrum, Kanban, and Lean Development, have become increasingly popular. These methodologies allow enterprises to respond swiftly and effectively to the unpredictable nature of the software industry. In this race to embrace agility, many organizations have adopted the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe). SAFe is a globally recognized framework that scales Agile practices to an enterprise level, ensuring projects are delivered on time, with high quality and maximum business value. To effectively utilize the power of SAFe, understanding the specific roles in the framework is crucial. A couple of these roles, such as the Release Train Engineer and Solution Architect, are critical in aligning efforts of large teams and funneling work effectively to deliver valuable outcomes.
Deciphering the Role of a Release Train Engineer (RTE)
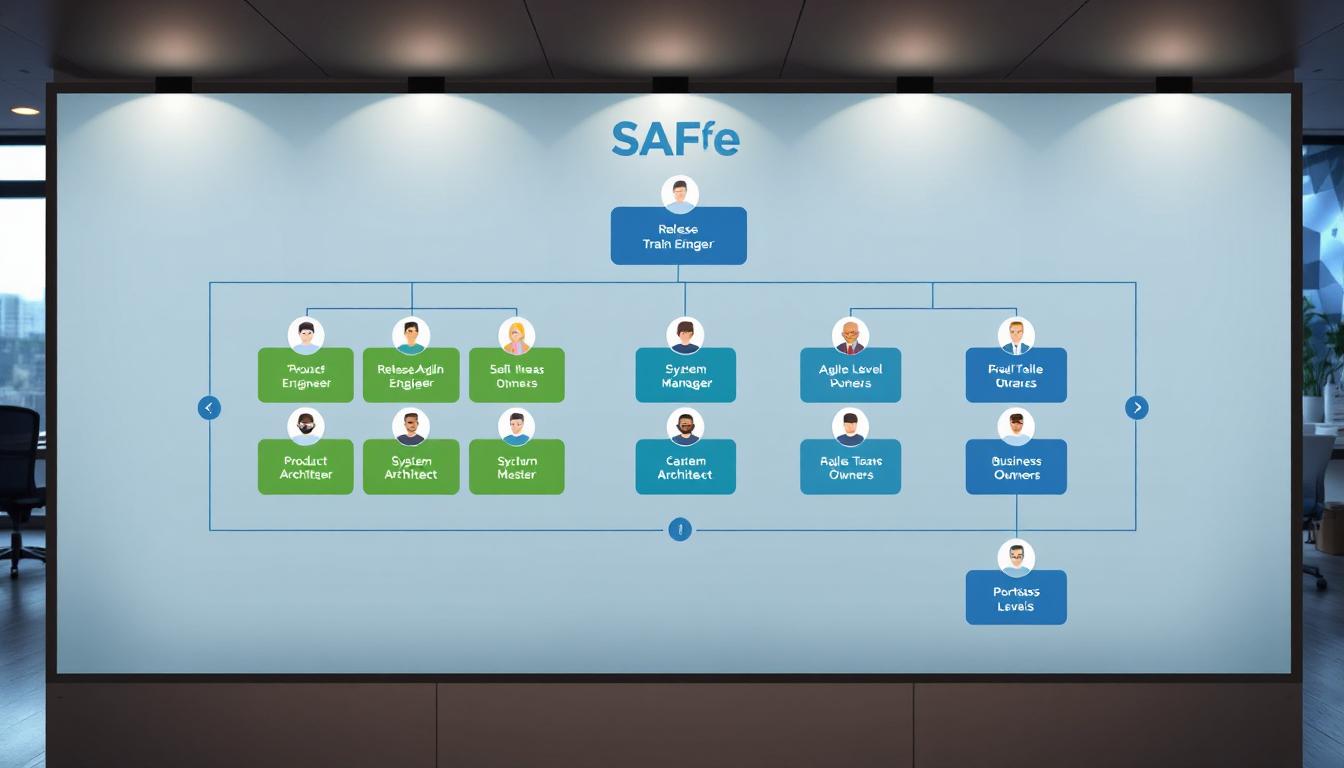
The Release Train Engineer (RTE) is a unique role within the SAFe framework that plays a pivotal role in ensuring smooth operations. The RTE is the leader of the Agile Release Train (ART). This role is akin to the Scrum Master role at a team level, but they operate at a program level, coordinating multiple Agile teams in one train.
As a servant leader and coach for an Agile Release Train (ART), the RTE’s responsibilities include:
- Leading the ART: The RTE steers the ART towards achieving a shared vision and purpose. They ensure effective and efficient work flows within and across self-organizing teams.
- Assisting Teams: The RTE helps remove obstacles and roadblocks that might impede the progress of the teams in their pursuit of delivering valuable software increments.
- Facilitating Interaction: The RTE promotes cross-team communication and collaboration. By encouraging an open and transparent environment, they help create a cohesive and productive work culture.
- Driving Continuous Improvement: The RTE encourages teams to self-reflect and improve their processes for more efficient and effective software development.
Unveiling the Role of a Solution Architect
Another critical role within the SAFe framework is the Solution Architect. They provide technical leadership and architectural vision to entire ARTs, working hand-in-hand with teams to create practical solutions that align with organizational goals. Their role is primarily focused on architecting and designing best-in-class solutions to complex business problems.
Key responsibilities of a Solution Architect in SAFe include:
- Envisioning Strategies: The Solution Architect creates a high-level vision for the architecture that aligns with enterprise goals.
- Technical Roadmapping: The Solution Architect is responsible for devising a technical roadmap that helps guide the ART’s implementation strategies.
- Ensuring Solution Effectiveness: Solution Architects work closely with development teams and stakeholders to ensure the developed solution meets all the required business and technical requirements and can be efficiently integrated into the existing system.
- Guiding Teams: They provide guidance and mentorship to teams on architecture and design issues, helping them navigate key technical decisions.
Collaboration of RTE and Solution Architect in SAFe
The collaboration between the RTE and Solution Architect is critical to deliver value at scale. Both roles carry unique responsibilities, but they are intertwined in their endeavor to align large teams and ensure successful software delivery.
The Solution Architect provides the necessary technical and architectural guidance, developing a vision and a plan which the RTE helps translate into executable strategies for the Agile teams. Together, they support the communication and cooperation required to drive enterprise success.
Challenges in Role Execution
Despite the clearly defined responsibilities, both RTE and Solution Architects often face challenges in executing their roles. Balancing technical aspects with business outcomes, facilitating good communication among a large number of team members, ensuring smooth workflow amidst changing project requirements, and maintaining continuous delivery of valuable software are some common obstacles encountered.
Conclusion: Value of Agile Roles in SAFe
In conclusion, the roles of Release Train Engineer and Solution Architect in the SAFe framework are challenging but vital. Proper execution of these roles can lead to the creation of high-quality software delivered in a timely manner, thereby driving effective alignment among teams and delivering value at scale. Organizations adopting SAFe need to ensure these roles are precisely defined and individuals assuming these roles have the necessary skills to guide their Agile Release Trains successfully.